Translating Site Content with WorldView
Use WorldView to create, manage, and publish your translated content within Ingeniux CMS. The WorldView feature controls globalization settings, language mapping, and page translation workflows. With WorldView, you can customize content so that visitors and contributors can interact with your site in different languages. Only administrators can change WorldView settings and execute the actual clone operations (i.e., Paste as Clone, Paste New Region Root).
For large translation projects or if your organization works with third-party translation services, you may want to extend WorldView's language-management capabilities through Translation Manager (TM). TM lets you send and receive work to and from third-party translation services, and, most importantly, synchronize that work across CMS pages.
In the CMS, a master page contains the original version of a page, while a clone page is the version intended for translation, which is copied from a master. Master and clone pages map and exist in relation to each other (i.e., master pages map to clone pages, and vice versa).
We use the term region root to describe locale-specific collections in the Site Tree.
WorldView Scenario
In multi-lingual projects, master/clone relationships can become complex. You may have scenarios where more than one master collection exists. For example, suppose you are part of a start-up business that originated in the United States. In its first year, your organization's web portal was in English to meet the needs of English-speaking customers in the U.S. and a few customers in British Columbia, Canada.
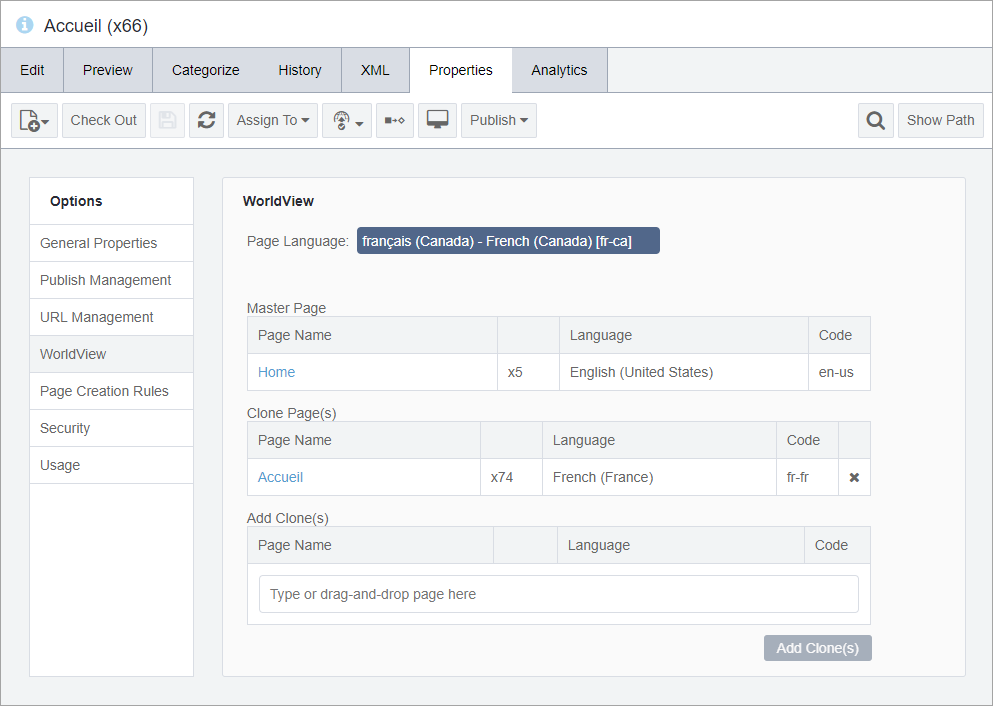
In its second year of operation, your organization gained French-speaking customers from Quebec, Canada, who required portal content from your site. To accommodate your new translation needs, you set up WorldView so that your original English (en-us) content is assigned as the master region root in the CMS Site Tree and a copy of the original English (i.e., the clone) was created in the Site Tree so that it could be translated to French (fr-ca).
In its third year of operation, your organization wins several large contracts from the European Union, namely from France (fr-fr) and Spain (es-es). To gain translation efficiencies, you set up the Canadian French (fr-ca) content, which had been translated in year two, as the master region root and have made a clone of this French (fr-ca) master to localize this clone for your customers in France. Because no Spanish localizations existed until year three, it's likely that you would set English (en-us) as the master region root and then designate a copy of the English (en-us) master as a new region root for Spanish (es-es). This cloned region root aids your Spanish translators as they localize your portal's content for Spanish (es-es) customers.
In the scenario above:
- The English (en-us) content is the master collection for the Canadian French (fr-ca) and Spanish (es-es) translations.
- The Canadian French region root is both:
- A clone of the English (master) content.
- The master region root for the French (fr-fr) locale.
- The Spanish region root is a clone of the English content.
All language collections are region roots but only two of them, namely English (en-en) and French (fr-ca), are master region roots. Once set up, the relationships among region roots are listed in Site > Properties tab > WorldView option. See Worldview Properties for details.
Complete the following steps to set up content for translation in WorldView:
- Administrators must complete the translation prerequisites.
- Prepare pages for translation in WorldView.
- Translate pages in the Translate tab.
- Optional: Add clone pages after the initial language assignments.
- Optional: Paste clones from master.
- Optional: Activate WorldView workflows.
This section includes:
